Cannabinoids
We have a list of synthetic cannabinoids – k2 and spice like 5F-ADB, AMB-FUBINACA for laboratory research and analytical studies from a reliable RC shop — NNRCHEM with overnight shipping in USA, Canada and EU. No “customs” or “hidden fees”.
represent a large and structurally diverse group of chemical compounds developed primarily for research into the endocannabinoid system and cannabinoid receptor pharmacology. These substances are supplied exclusively as high-purity analytical reference standards intended for use in forensic, toxicological, pharmaceutical, and academic laboratories.
What are synthetic cannabinoids?
Synthetic cannabinoids are man-made molecules designed to interact with the same cannabinoid receptors (primarily CB₁ and CB₂) that are activated by naturally occurring phytocannabinoids such as Δ⁹-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Unlike plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids are produced entirely through chemical synthesis and typically exhibit much higher binding affinity and potency at cannabinoid receptors.
The first compounds in this class were created in academic and pharmaceutical research settings during the 1990s–2000s to better understand cannabinoid receptor function, signal transduction pathways, and potential therapeutic targets. Well-known early examples include compounds from the aminoalkylindole family, such as JWH-018, and later series such as AM-, CP-, HU-, WIN-, and XLR-compounds.
Common nomenclature and categories
The synthetic cannabinoid family is usually grouped by chemical scaffold. The most frequently referenced structural classes include:
- Naphthoylindoles (e.g., JWH-018, JWH-073, JWH-200, AM-2201)
- Phenylacetylindoles (e.g., JWH-250, JWH-203)
- Benzoylindoles (e.g., RCS-4, AM-694)
- Cyclohexylphenols (e.g., CP 47,497 and its C8 homologue)
- Tetramethylcyclopropylindoles (e.g., UR-144, XLR-11)
- Adamantoylindoles (e.g., AM-1248, APICA)
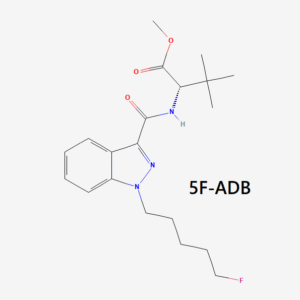
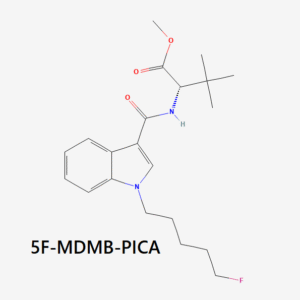
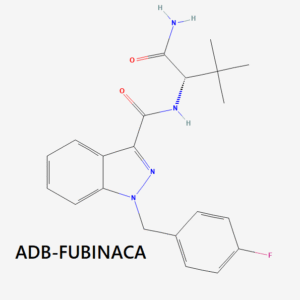
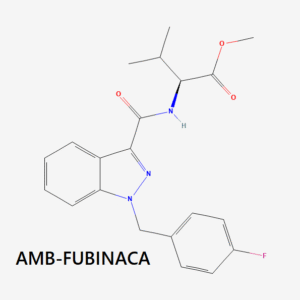
- Indazole-based compounds (e.g., AB-FUBINACA, ADB-FUBINACA, 5F-ADB, MDMB-4en-PINACA)
Many of these structural families have generated dozens of closely related analogues, resulting in hundreds of documented synthetic cannabinoids.
Legitimate scientific and analytical applications
Certified reference materials of synthetic cannabinoids and their metabolites are used in the following areas:
- Development and validation of analytical methods (GC-MS, LC-MS/MS, HRMS)
- Identification and confirmation of substances in seized materials
- Toxicological analysis of biological specimens (blood, urine, oral fluid, hair, tissues)
- Pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies
- Structure-activity relationship (SAR) investigations
- Receptor binding, functional assays, and signal transduction research
- Preparation of quality control samples and proficiency testing materials
Laboratories performing these activities require accurately characterized, high-purity standards with documented purity, identity, and stability data.
Regulatory status and important compliance notes
Most synthetic cannabinoids, including well-known compounds such as JWH-018, are classified as controlled substances in many jurisdictions:
- United States — Schedule I (most compounds)
- Canada — Schedule II or analogous list
- European Union — controlled under national laws and/or EU early-warning system / risk-assessment procedures
- United Kingdom — Class B or psychoactive substances legislation
- Many other countries — similar restrictive scheduling
All products in this category are supplied strictly for research and analytical purposes. They are not intended for human or veterinary consumption, diagnostic use, therapeutic use, or any form of in-vivo administration. Customers must hold all required licenses, permits, and authorizations mandated by national and international regulations governing controlled substances and precursor chemicals.
Quality and sourcing standards
Reputable suppliers of synthetic cannabinoid reference standards provide:
- Purity typically ≥98% (often ≥99%) determined by HPLC, GC-FID, or qNMR
- Full certificate of analysis (CoA) including chromatographic purity, identity (NMR, IR, MS), and batch-specific data
- Isotopically labeled internal standards when available
- Stable isotope-labelled analogues for quantitative applications
- Storage and handling recommendations to maintain integrity
- Traceable documentation back to synthesis and characterization steps
Trace impurities, regioisomers, and synthetic by-products are minimized and clearly reported when relevant.
Commonly referenced compounds in analytical work
Some of the most frequently requested synthetic cannabinoids in forensic and toxicological reference libraries include:
- JWH-018
- JWH-073
- JWH-250
- AM-2201
- UR-144
- XLR-11
- AB-FUBINACA
- ADB-FUBINACA
- 5F-ADB / 5F-MDMB-PINACA
- MDMB-4en-PINACA
- 4F-MDMB-BINACA
- JWH-018 N-pentanoic acid metabolite
- 5F-ADB metabolite M2
Many laboratories maintain extensive panels covering both parent compounds and major phase I metabolites to support comprehensive screening and confirmation workflows.
Synthetic cannabinoids constitute one of the most structurally diverse classes of research compounds studied in modern pharmacology and analytical chemistry. High-quality analytical reference standards of these substances play a critical role in method development, identification, quantification, and toxicological interpretation across forensic, clinical, and academic laboratories worldwide.
All materials in this category are provided exclusively for legitimate research and analytical purposes and must be handled in full compliance with applicable national and international regulations.
Explore the individual product pages to view detailed specifications, certificates of analysis, safety data sheets, and current availability for each reference standard.
Showing all 4 results
-
Cannabinoids
5F-ADB
-
Cannabinoids
5F-MDMB-2201
-
Cannabinoids
ADB-FUBINACA
-
Cannabinoids
AMB-FUBINACA